Town & City Data Dashboards: Transforming Urban Insights into Action | townstats.live
Wiki Article
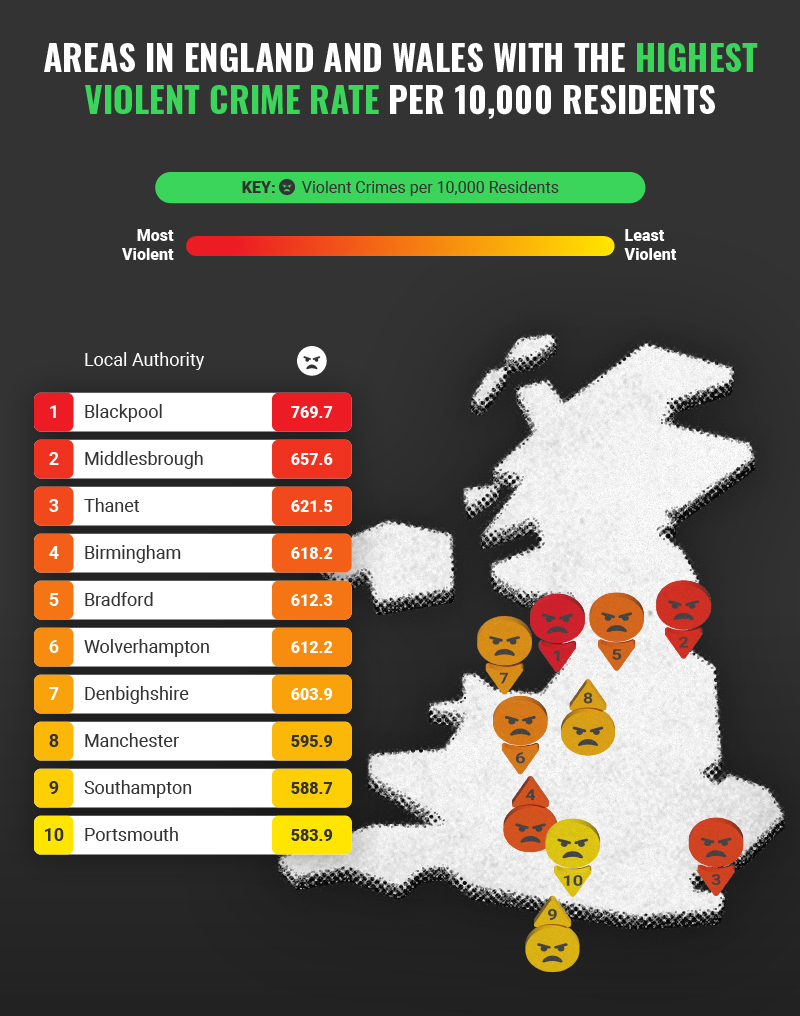
In the modern age of data, towns and cities around the world are turning raw information into meaningful insights through data dashboards. These digital platforms aggregate, visualize, and present data from multiple sources — giving policymakers, municipal staff, and residents a clear and dynamic view of how communities are functioning. From tracking public services and economic trends to monitoring sustainability and safety metrics, town and city data dashboards have become indispensable tools for evidence-based decision-making and civic engagement. Check this out: crime information about a town
What Is a Town & City Data Dashboard?
A data dashboard is an interactive interface that displays real-time or regularly updated data through charts, maps, tables, and indicators. Think of it as a central control panel for a city’s key performance measures. Instead of sifting through spreadsheets or static reports, users can quickly explore trends, compare indicators, and understand complex information at a glance.
Dashboards are tailored to specific audiences:
City managers and planners focus on operational metrics.
Elected officials monitor outcomes tied to policies and budgets.
Residents and businesses explore community trends like housing, safety, or traffic.
Researchers and journalists use dashboards to analyze patterns and generate stories.
Core Components of a City Data Dashboard
Most effective dashboards include some combination of the following:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Quantitative measures that reflect the health of city functions — such as crime rates, public transportation ridership, water quality, or budget performance.
Visualizations: Graphs, heatmaps, timelines, and pie charts that illustrate patterns and trends.
Data Filters: Tools that allow users to explore data by location, date range, demographic groups, or service category.
Geospatial Maps: Interactive maps that display spatial data such as traffic counts, public assets, or service requests.
Download & API Access: For advanced users, the ability to download data or connect to dashboard data streams via APIs (Application Programming Interfaces).
Together, these elements create a user-friendly environment where data is not just stored, but actively used to support decisions and inform the public. Check: prayer times for a town
Why Cities Use Data Dashboards
The adoption of dashboards by local governments has accelerated over the past decade for several key reasons:
1. Transparency and Accountability
Citizens want to know how their tax dollars are spent and how well public programs are performing. Dashboards make government data more accessible and understandable, fostering trust and civic engagement. A resident curious about response times for service requests or infrastructure investment can explore this data directly — without filing formal requests.
2. Real-Time Insights for Decision-Making
Traditional reporting can lag weeks or months behind reality. With dashboards that update frequently — sometimes in real time — municipal leaders can detect emerging issues early. For example, spikes in emergency calls, traffic congestion, or utility outages can be identified quickly and addressed proactively.
3. Performance Management
Dashboards help cities set goals and measure progress. Whether the priority is reducing crime, increasing recycling rates, or improving road maintenance, performance metrics are clearly defined and monitored. This enables data-informed budgeting and targeted program improvements.
4. Interdepartmental Collaboration
Data dashboards break down silos between departments. When transportation, public works, health services, and economic development teams see the same data, it encourages coordinated strategies and shared objectives.
Use Cases: How Dashboards Drive Impact
Municipal dashboards are versatile and span many domains:
Public Safety: Dashboards display crime statistics, response times, and fire incidents, helping law enforcement and first responders allocate resources more efficiently.
Transportation & Traffic: Visualizations of transit ridership, bike-share usage, and traffic flows support planning for congestion relief and infrastructure investments.
Economic Data: Job growth, business permits, and investment trends inform economic development strategies.
Health & Environment: Cities track air quality, water usage, waste management, and pandemic indicators to protect public health and sustainability.
Citizen Services: Service request tracking dashboards show open issues like potholes, graffiti, or streetlight outages — and reveal how quickly they’re resolved.
Challenges & Best Practices
While dashboards are powerful, they must be thoughtfully designed:
Data Quality: Reliable dashboards depend on accurate and consistent data sources.
User Accessibility: Interfaces should be intuitive and accessible, including for users with disabilities.
Privacy & Security: Sensitive information should be protected, with appropriate aggregation and anonymization where needed.
Maintenance: Dashboards require ongoing updates and governance to stay relevant and useful.
Best practices include simple design, clear explanations of metrics, regular data refreshes, and channels for user feedback. Visit: school holidays of town
The Future of Urban Data Dashboards
As cities grow smarter, dashboards will evolve with predictive analytics, machine learning insights, and deeper integration across urban systems. Residents may soon explore city data using voice assistants or immersive visualizations. The trend points toward more open, interactive, and actionable platforms, empowering communities to make smarter decisions and build more resilient, equitable places to live.
For more information visit our website: https://townstats.live/